
台灣原生種食蟲植物為主,外來種為輔,致力於提升大眾對食蟲植物保育的認識與關注。相較於人們熟知的豬籠草與捕蠅草,台灣本土食蟲植物往往被忽略。隨著環境變遷與棲地破壞,部分品種已被列入保育等級。本專題透過視覺資訊設計、立體書籍與互動體驗,讓大眾在閱讀與動手實作中理解食蟲植物的獨特生存機制,並強化生態教育與永續理念。
Focusing primarily on Taiwan’s native carnivorous plants, with non-native species as a supplement, this project aims to raise public awareness and understanding of carnivorous plant conservation. Compared to well-known species like pitcher plants and Venus flytraps, Taiwan’s indigenous carnivorous plants are often overlooked. With environmental changes and habitat destruction, some species have been classified under conservation status. Through visual information design, pop-up books, and interactive experiences, this project allows the public to explore the unique survival mechanisms of carnivorous plants through reading and hands-on activities, reinforcing ecological education and sustainability concepts.
關於食蟲植物
About Carnivorous Plants
食蟲植物屬於特別生物的一類,多數生長於日照充足的泥濘濕地,那裡是個貧瘠偏酸的環境,因周遭沒有肥沃的土壤,棲地的氮及其他植物生長所必須之營養容易被沖刷流失,經過長期演化與天擇結果,因此演化出捕捉及分解動物以補充棲地內營養的型態構造,造就了它們特殊的生存方式。
Carnivorous plants belong to a special category of organisms. Most of them grow in sunny, muddy wetlands, which are poor, acidic environments. Due to the lack of fertile soil in the surroundings, the nitrogen and other essential nutrients for plant growth are easily washed away. As a result of long-term evolution and natural selection, these plants have developed structures that capture and decompose animals to supplement the nutrients in their habitats, leading to their unique survival strategies.

絕種危機
Extinction Crisis
由於台灣在這幾年的土地開發、化學肥料和除草劑廣泛使用等的人為因素,另外也因爲攔沙壩興築後,土地逐漸旱化、養份含量升高,使得當地濕地植物的優勢不再,而讓台灣的原生食蟲植物族群已面臨滅絕危機。
Due to human factors such as land development, widespread use of chemical fertilizers and herbicides in recent years, as well as the construction of sand retention dams, the land has gradually become arid, and the nutrient content has increased. As a result, the dominance of wetland plants in the area has diminished, putting Taiwan’s native carnivorous plant species at risk of extinction.




茅膏菜
Drosera
茅膏菜屬包含多個物種,其中一些物種被列為受威脅物種。
The genus Drosera includes multiple species, some of which are listed as threatened species.
長葉茅膏菜
Drosera longifolia
未在IUCN紅色名錄中單獨列出,可能被視為其他物種的同物異名。
Not listed separately in the IUCN Red List, it may be considered a synonym of another species.
小毛氈苔
Drosera spatulata
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
寬葉毛氈苔
Drosera intermedia
被列為無危物種。
Listed as a Least Concern (LC) species.



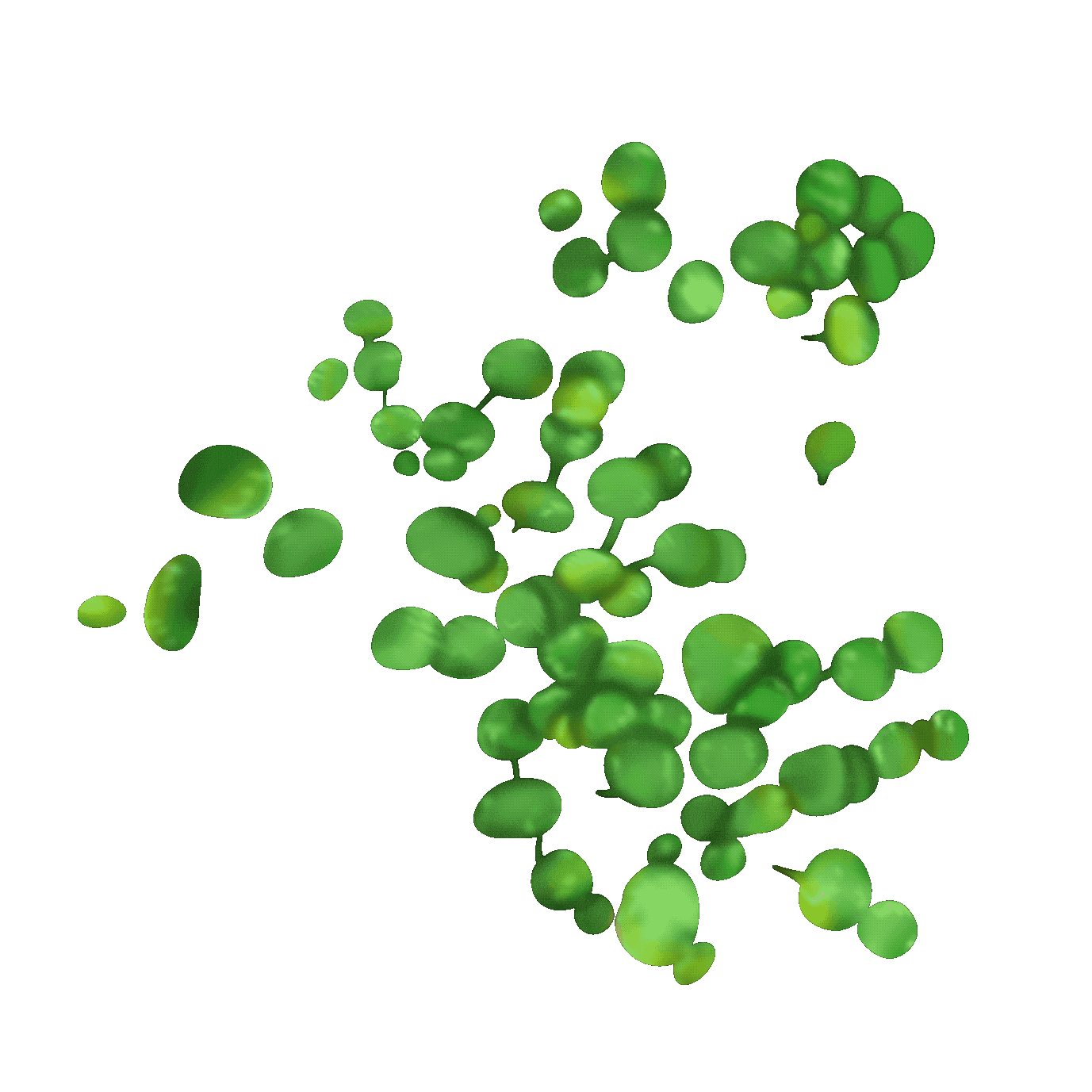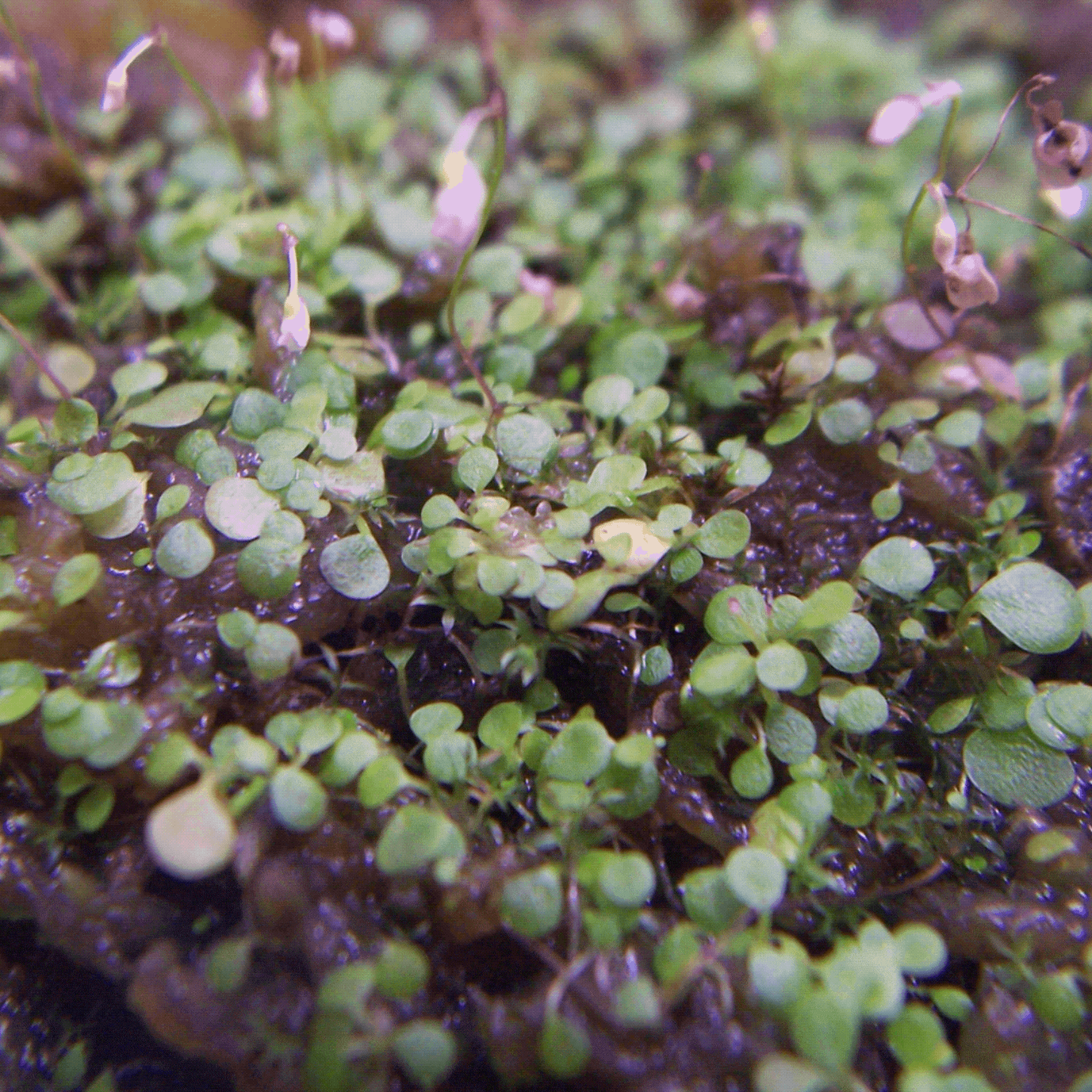
黃花狸藻
Utricularia aurea
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
南方狸藻
Utricularia australis
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
絲葉狸藻
Utricularia striatula
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
圓葉狸藻
Drosera rotundifolia
被列為無危物種。
Listed as a Least Concern (LC) species.




兩裂狸藻
Utricularia dichotoma
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
短梗挖耳草
Drosera brevipes
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
齒萼挖耳草
Drosera binata
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
捕蠅草
Dionaea muscipula
被列為易危物種。
listed as a Vulnerable (VU) species.


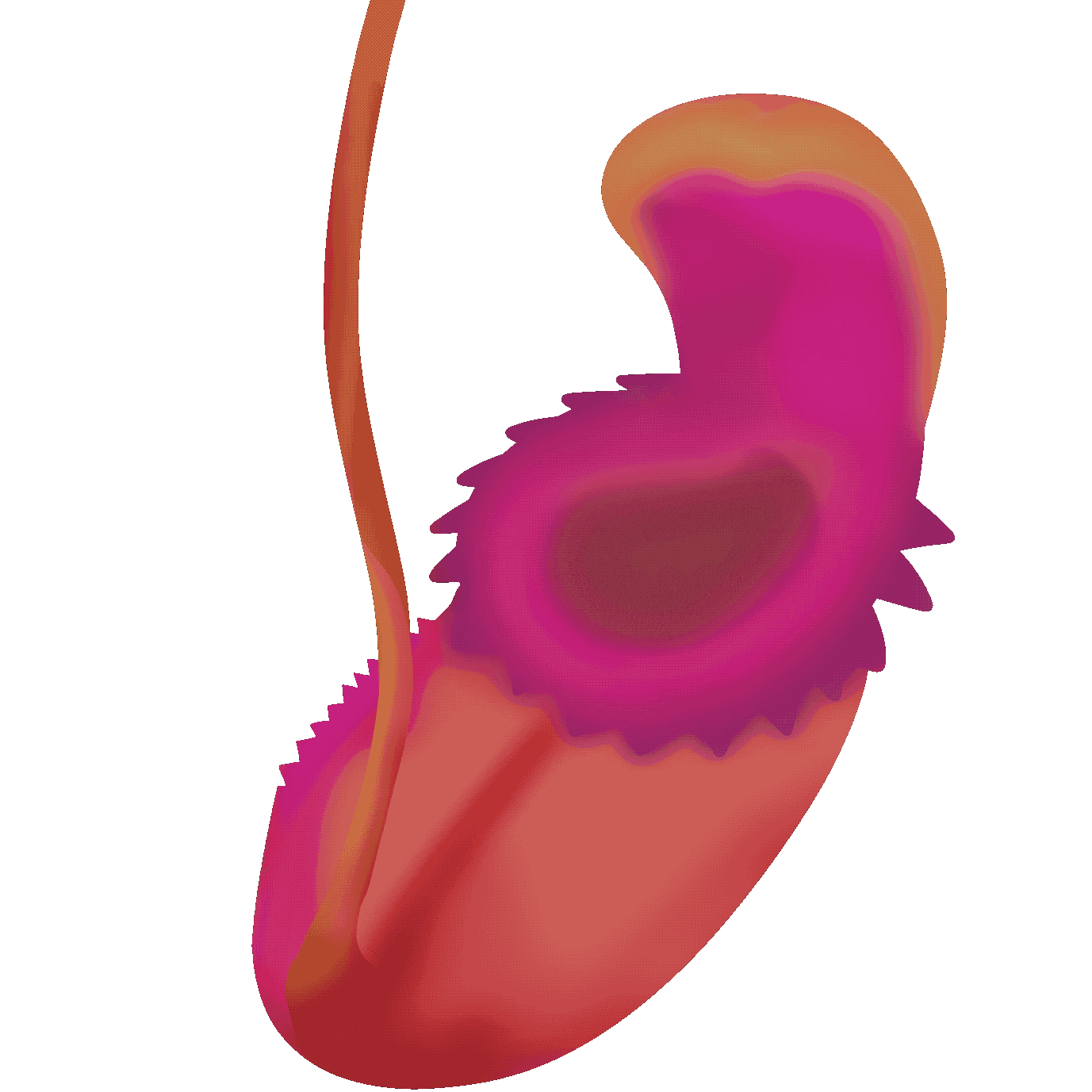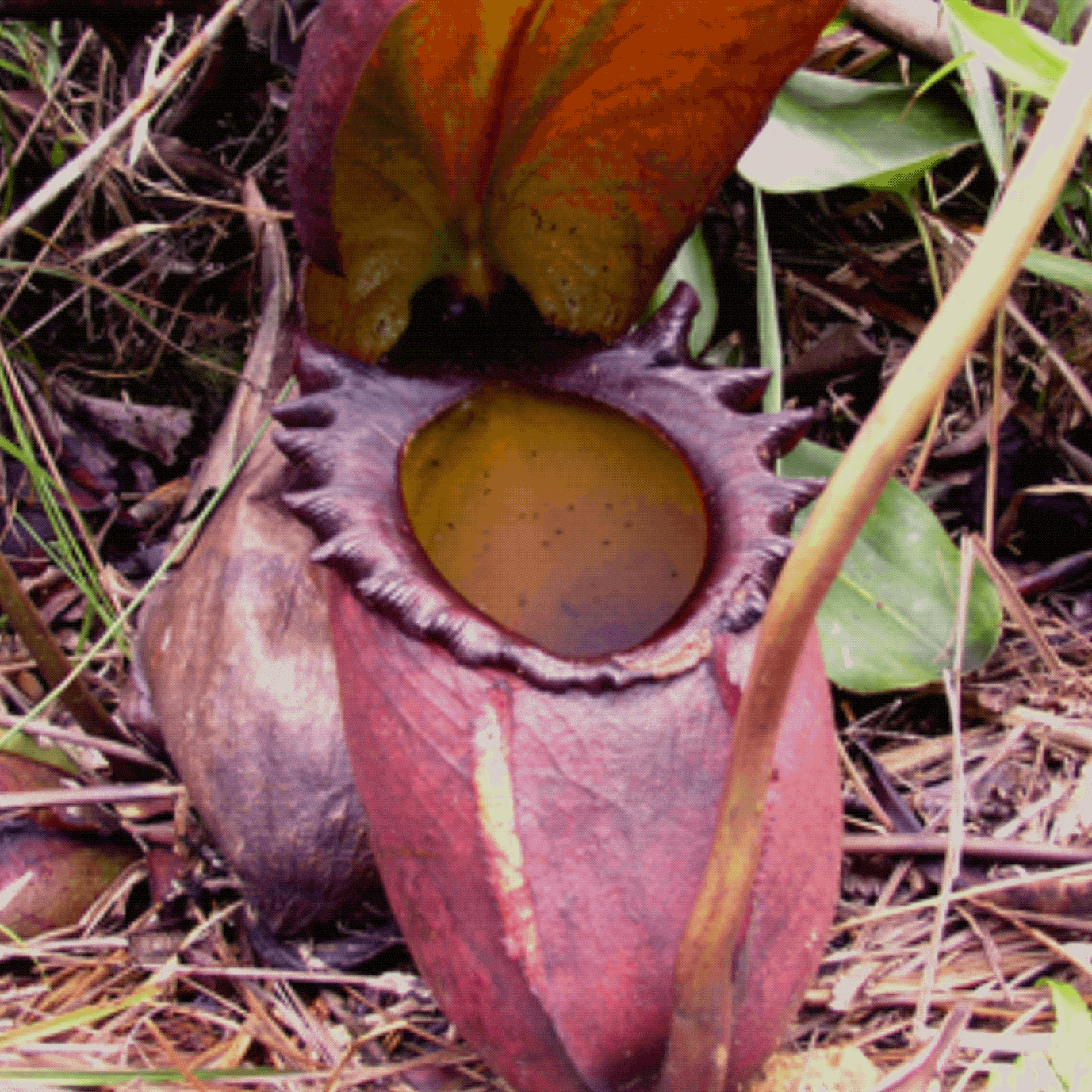

紅色食人魚捕蠅草
Dionaea muscipula 'B52'
這是捕蠅草的栽培品種,未在IUCN紅色名錄中單獨評估。
This is a cultivar of the Venus flytrap, which has not been assessed separately in the IUCN Red List.
齒狀捕蠅草
Dionaea muscipula 'Dentate'
這是捕蠅草的栽培品種,未在IUCN紅色名錄中單獨評估。
This is a cultivar of the Venus flytrap, which has not been assessed separately in the IUCN Red List.
馬來王豬籠草
Nepenthes rajah
被列為極危物種。
Listed as a Critically Endangered (CR) species.
萊佛士豬籠草
Nepenthes rafflesiana
被列為無危物種。
Listed as a Least Concern (LC) species.
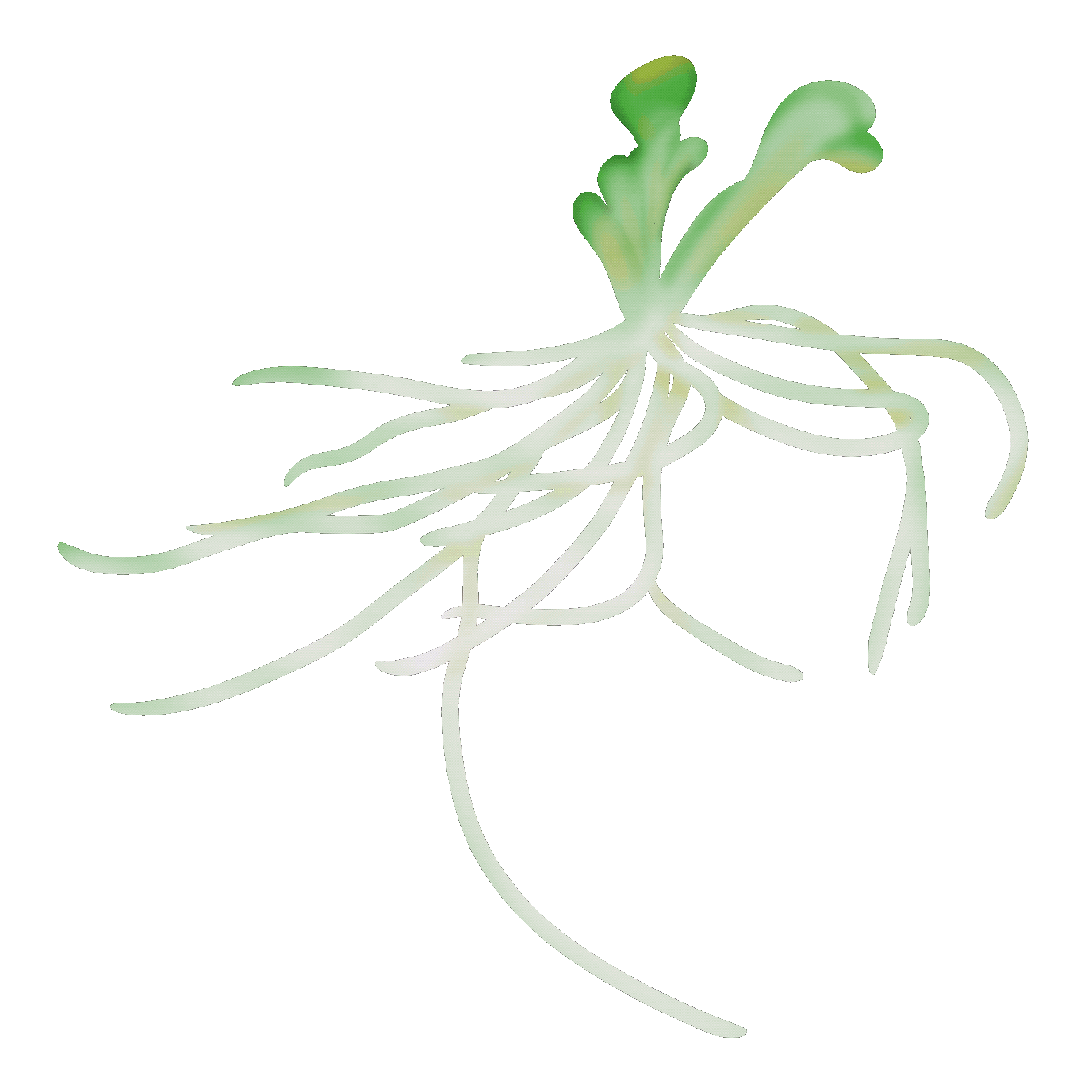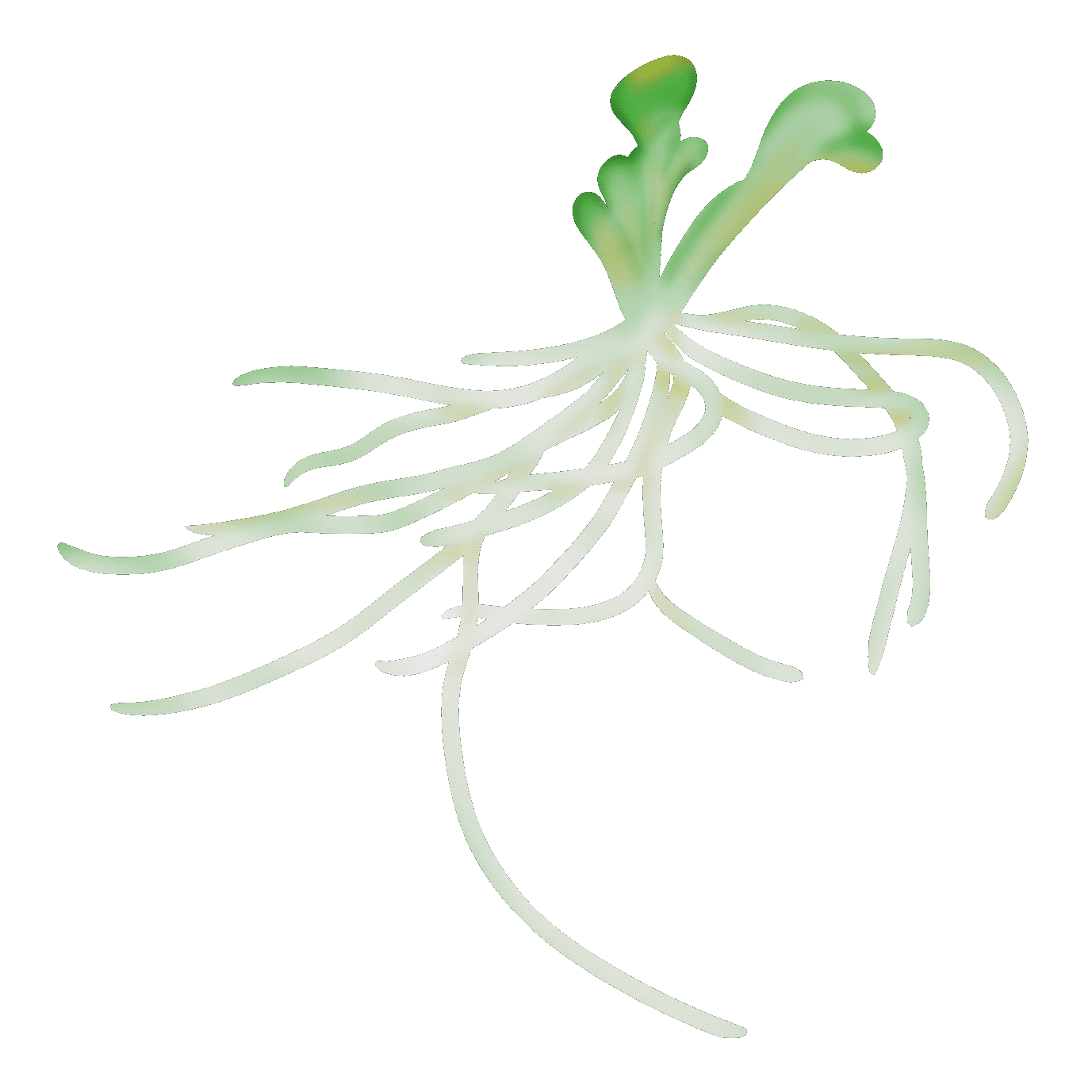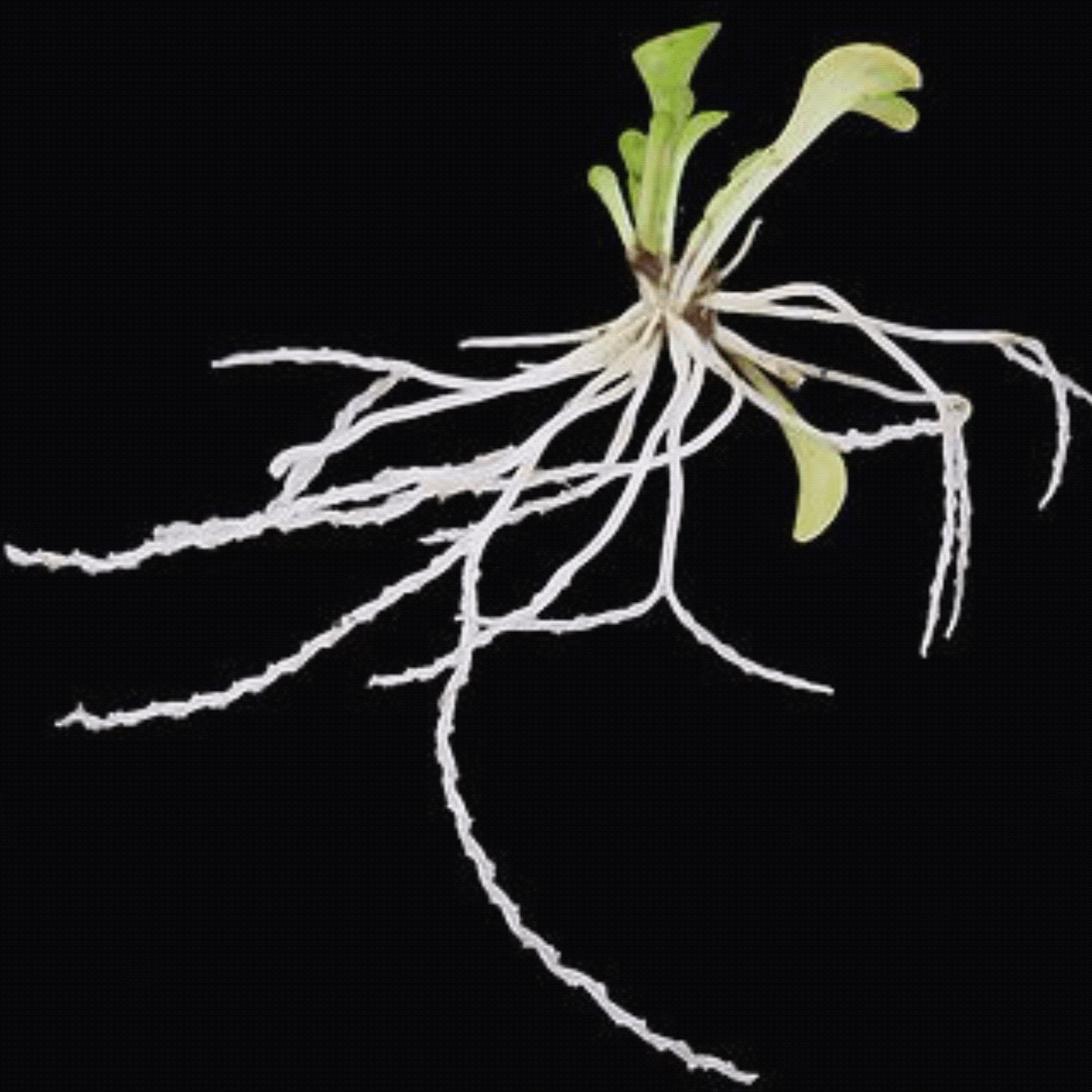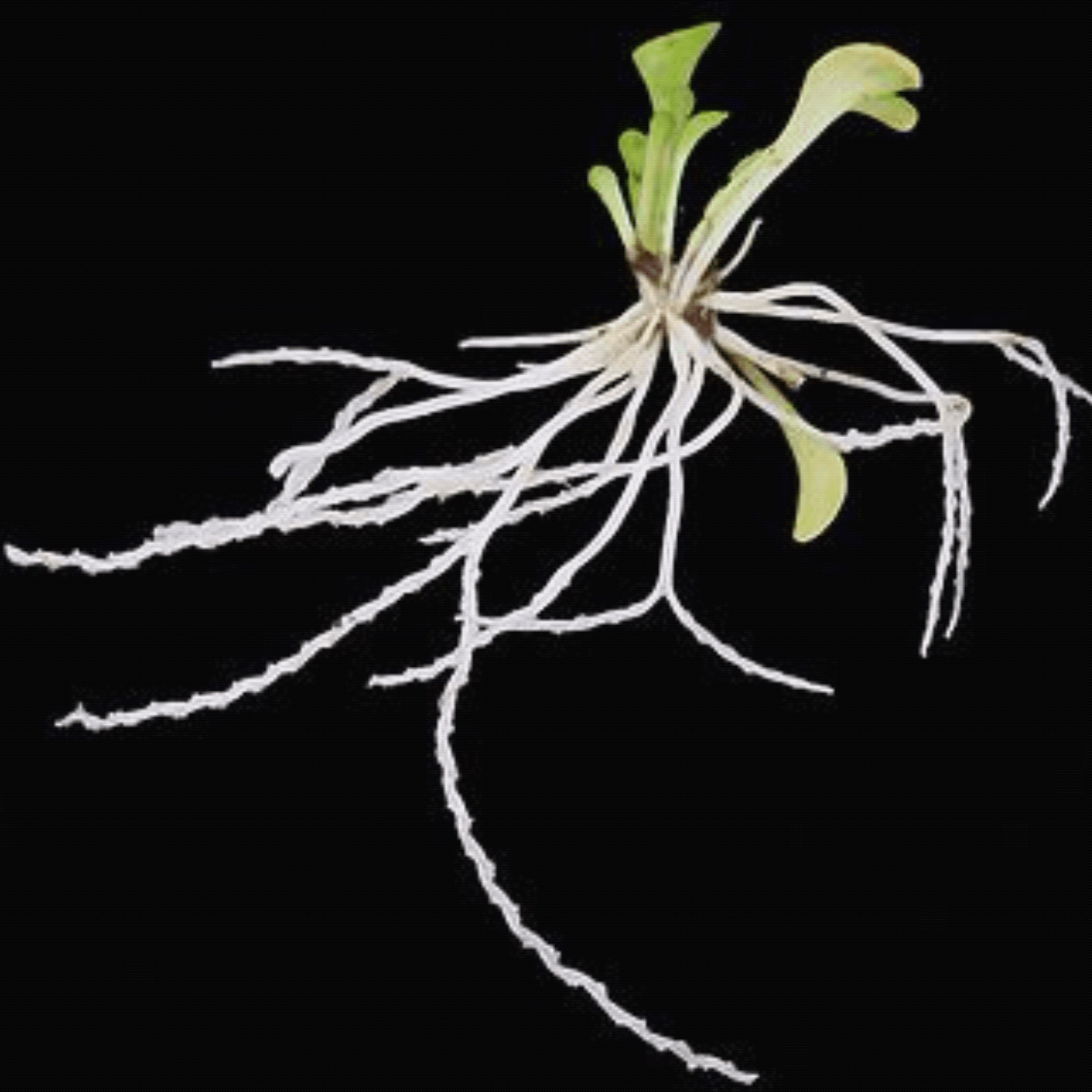



螺旋狸藻
Utricularia spiralis
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
葫蘆豬籠草
Nepenthes ampullaria
被列為無危物種。
Listed as a Least Concern (LC) species.
眼鏡蛇瓶子草
Darlingtonia californica
被列為無危物種。
Listed as a Least Concern (LC) species.
高山捕蟲堇
Pinguicula alpina
未在IUCN紅色名錄中列為受威脅物種。
Not listed as a threatened species in the IUCN Red List.
植物生存法則
The Rules of Plant Survival
由於土壤中的氮及其他植物生長所必須之營養非常缺乏,各式各樣的食蟲植物因而演化出捕蟲機制捕捉動物獲取營養。食蟲植物是由葉子特化形成捕捉昆蟲的工具,能夠分泌消化液分解動物的軀體為有機養份,但是它們捕蟲器官的構造、捕蟲的原理也都不盡相同。
Due to the severe lack of nitrogen and other essential nutrients for plant growth in the soil, various carnivorous plants have evolved mechanisms to capture animals in order to obtain nutrients. Carnivorous plants have specialized leaves that form tools for capturing insects and are capable of secreting digestive fluids to break down the bodies of animals into organic nutrients. However, their trapping structures and mechanisms for capturing prey vary widely.
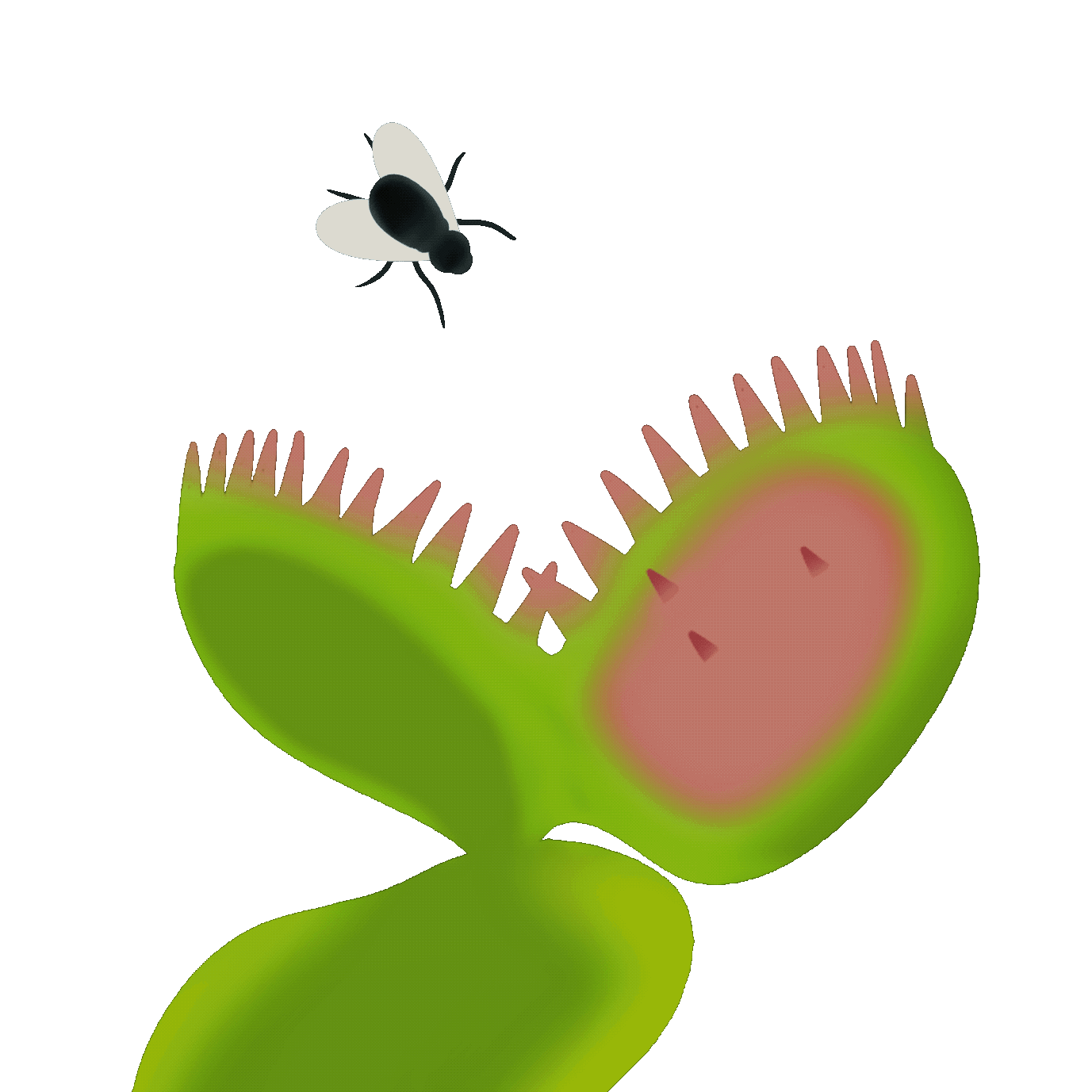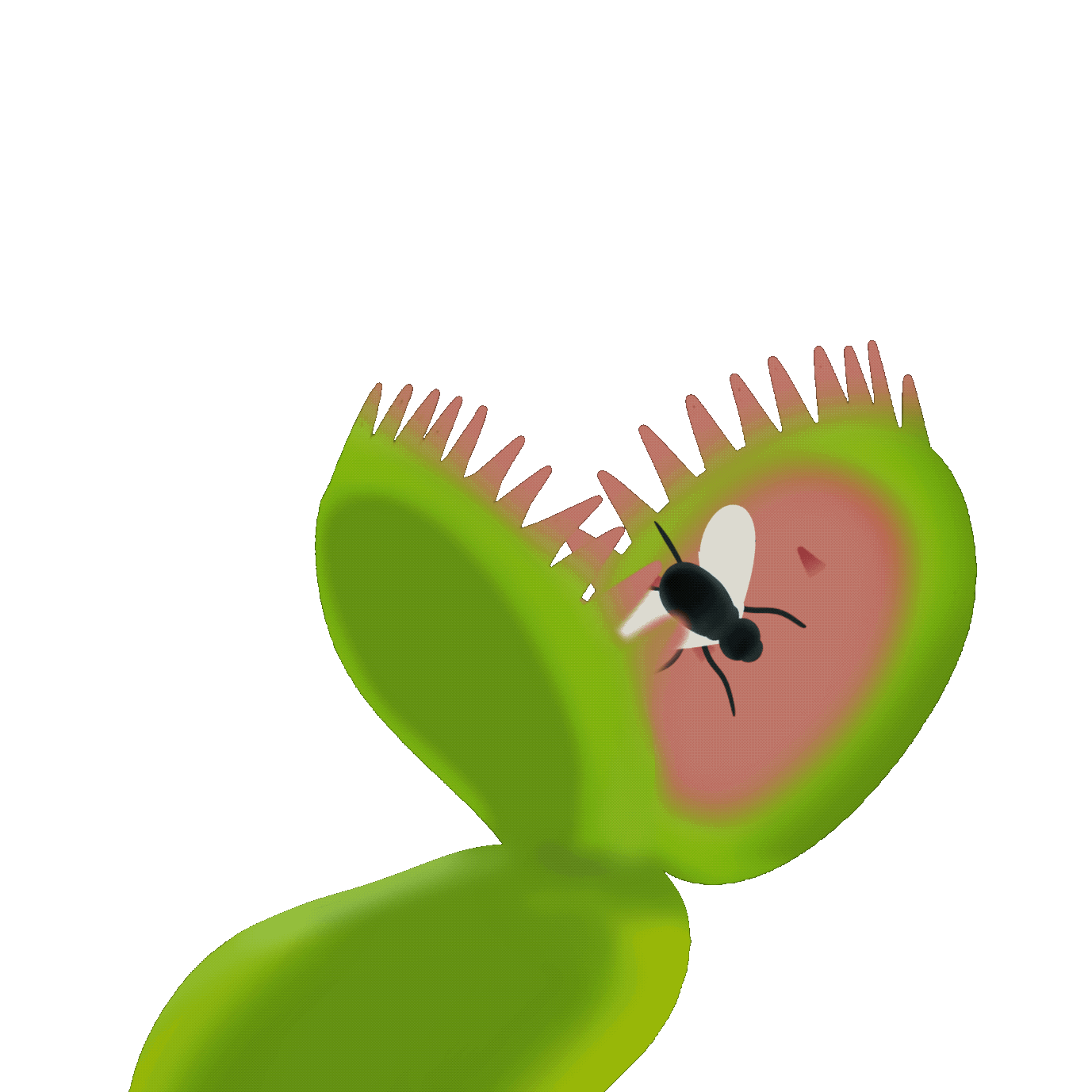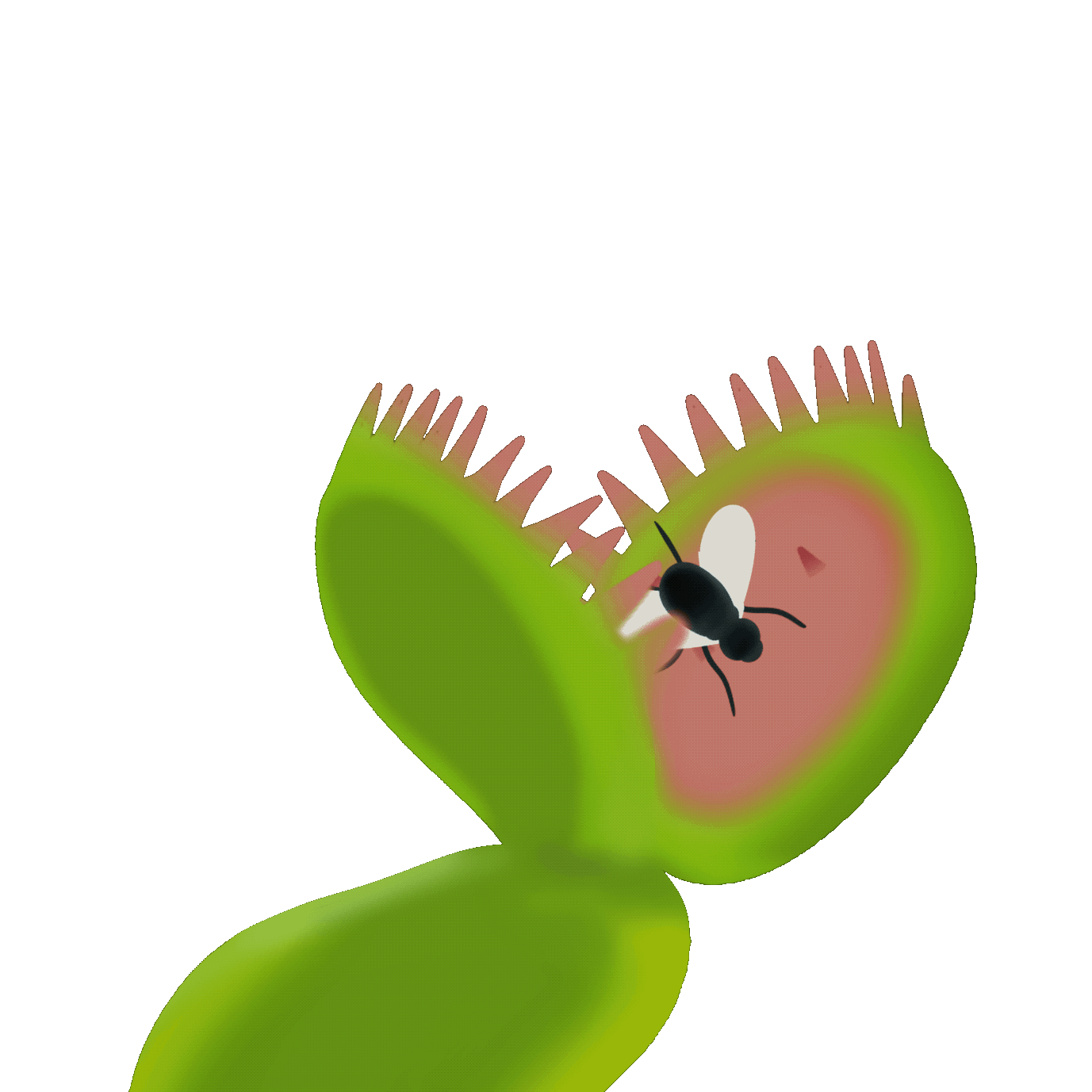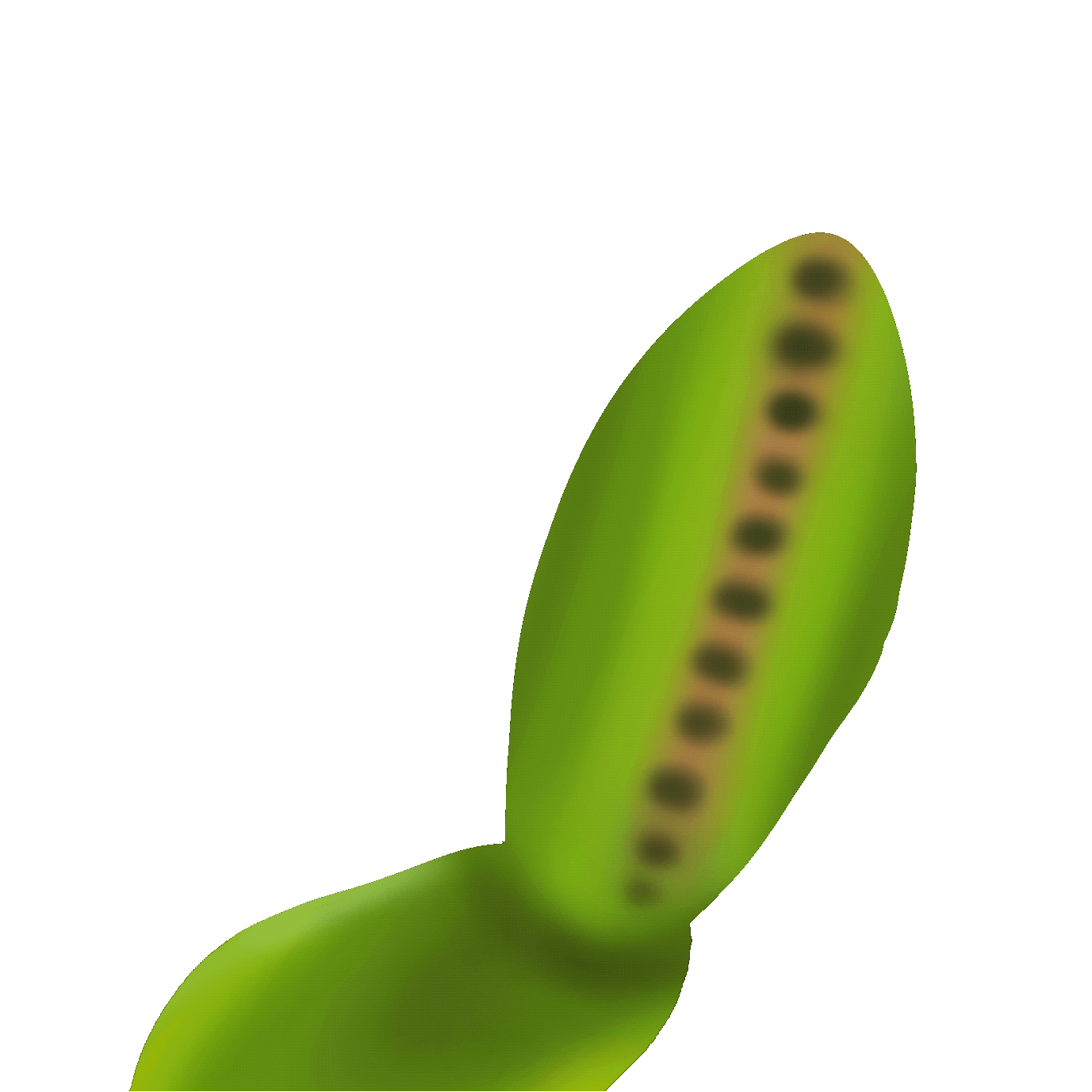
捕獸夾式
Snap traps
葉面上有細小的感應毛,當昆蟲觸碰到感應毛(通常需兩次接觸),葉片會迅速閉合,困住獵物。之後植物會分泌消化液,逐步分解昆蟲並吸收營養。
The leaf surface has small sensory hairs. When an insect touches the sensory hairs (usually requiring two touches), the leaf quickly closes, trapping the prey. Then, the plant secretes digestive fluids to gradually break down the insect and absorb its nutrients.
黏著式
the sticky “flypaper”
毛氈苔的葉面上長滿腺毛,腺毛頂端分泌黏稠的液體,類似露珠型態。當昆蟲接觸黏液時,會被牢牢黏住,掙扎時會進一步觸發更多腺毛包圍它。毛氈苔逐漸分泌消化酶,分解獵物並吸收養分。
The leaf surface of Drosera (sundews) is covered with glandular hairs that secrete a sticky liquid, similar to dew. When insects come in contact with the sticky substance, they become firmly stuck. Struggling causes more glandular hairs to surround the prey. The sundew gradually secretes digestive enzymes, breaking down the prey and absorbing the nutrients.

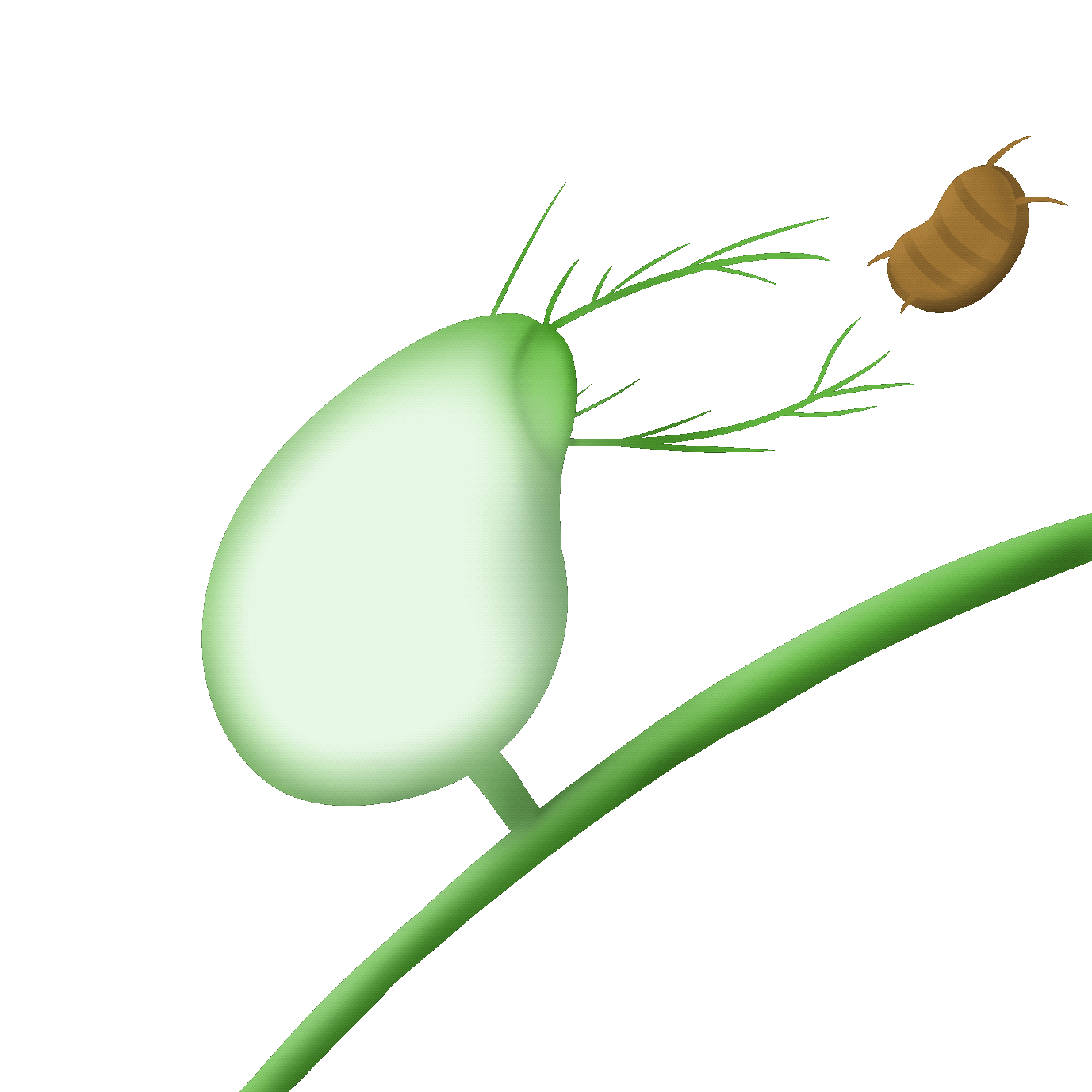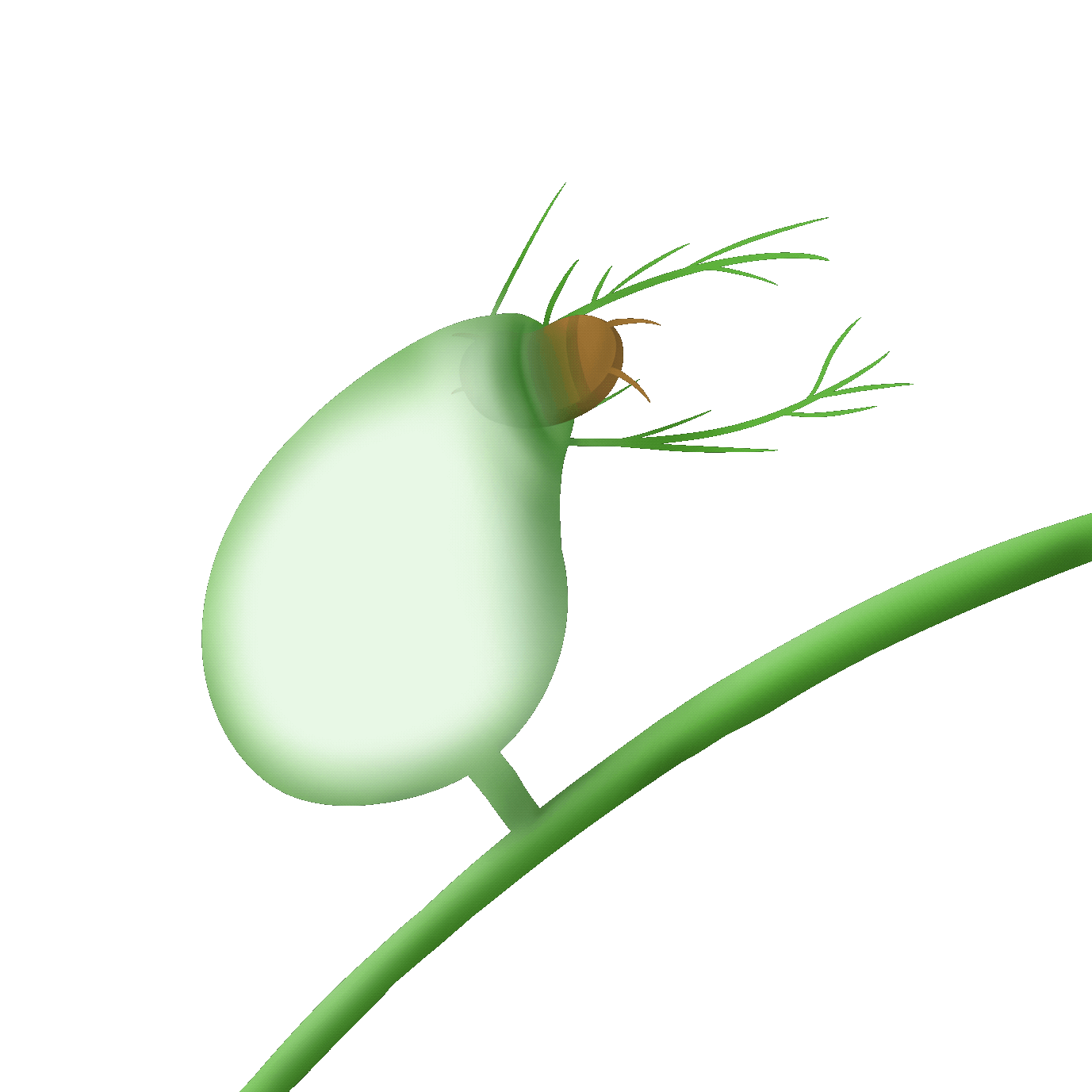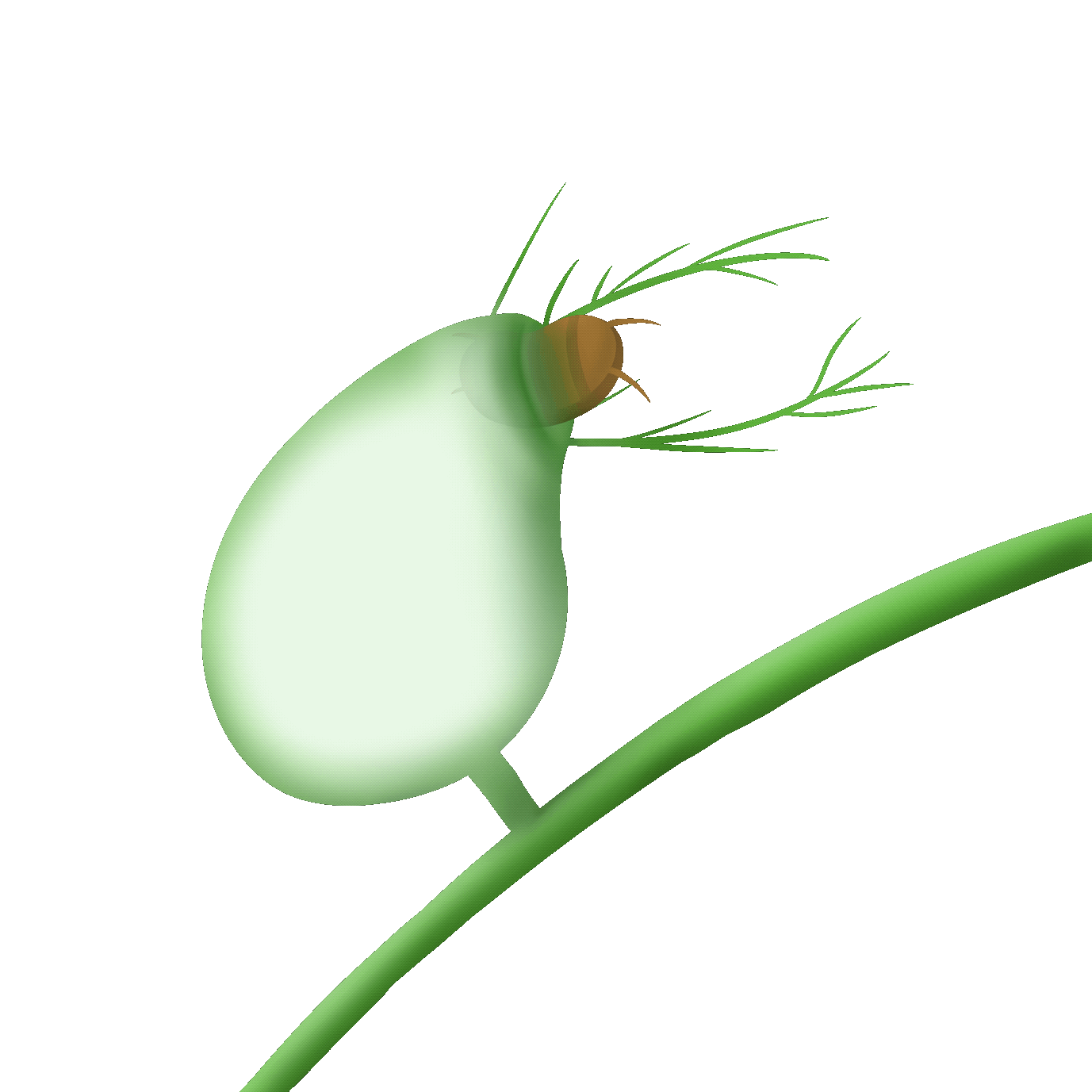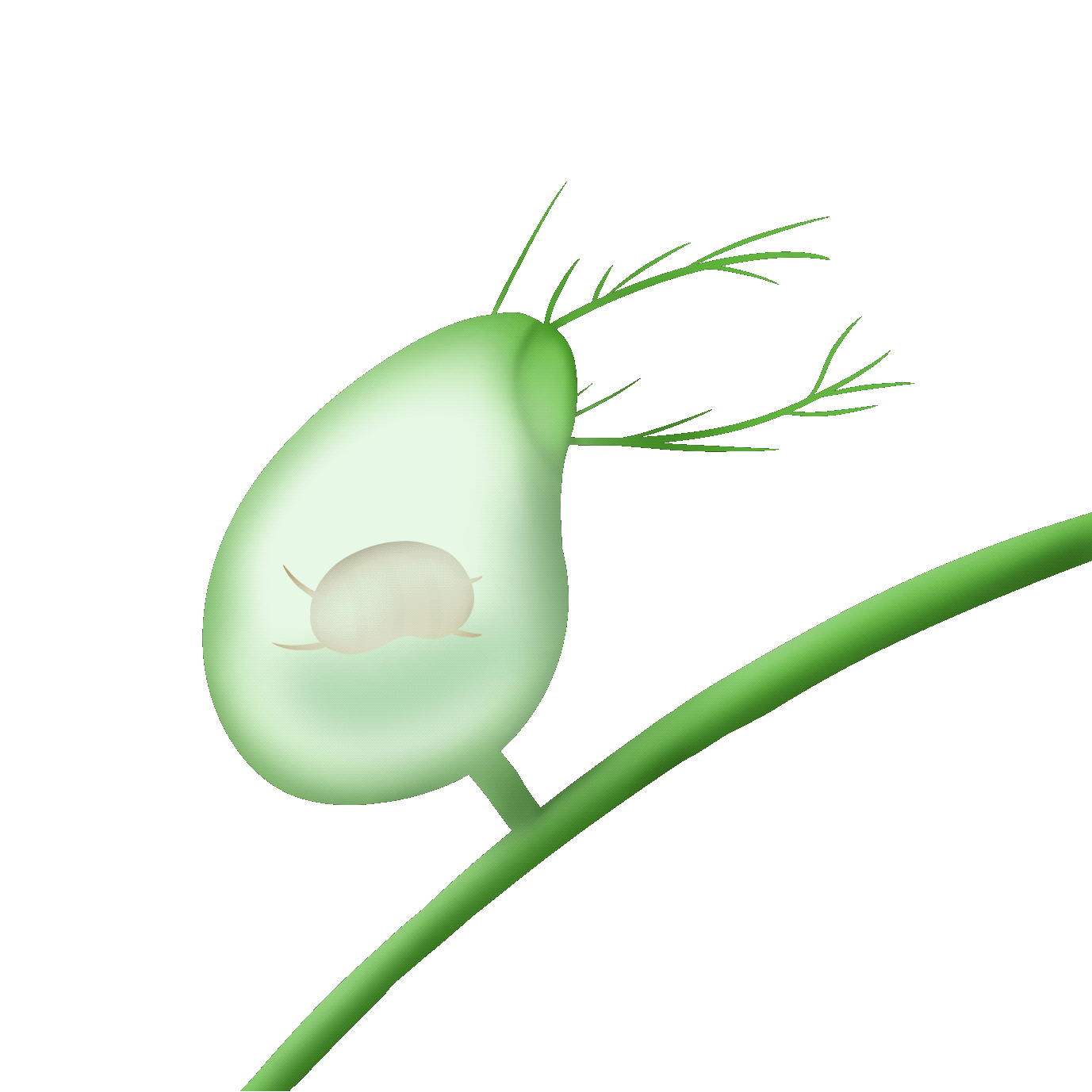
吸入式
the bladder trap
狸藻的陷阱是一個小囊袋,內部呈現負壓。當微小的水生生物碰到捕捉毛時,囊袋會迅速打開,將獵物吸入並關閉。捕獲的獵物會被分解並消化。
The trap of Utricularia (bladderwort) is a small sac that creates negative pressure inside. When tiny aquatic creatures touch the capturing hairs, the sac opens rapidly, sucking the prey in and closing. The captured prey is then broken down and digested.
陷阱式
the pitfall
豬籠草的葉片形成一個深杯狀的「籠子」,內部含有消化液。陷阱的邊緣通常分泌甜美的蜜汁吸引昆蟲,表面則非常光滑,使獵物滑落至消化液中溺斃。植物再利用酵素與細菌來分解獵物,吸收其營養。
The leaves of Nepenthes (pitcher plants) form a deep, cup-shaped "trap" containing digestive fluids. The edge of the trap typically secretes sweet nectar to attract insects, while the surface is very smooth, causing the prey to slip into the digestive fluid and drown. The plant then uses enzymes and bacteria to break down the prey and absorb its nutrients.

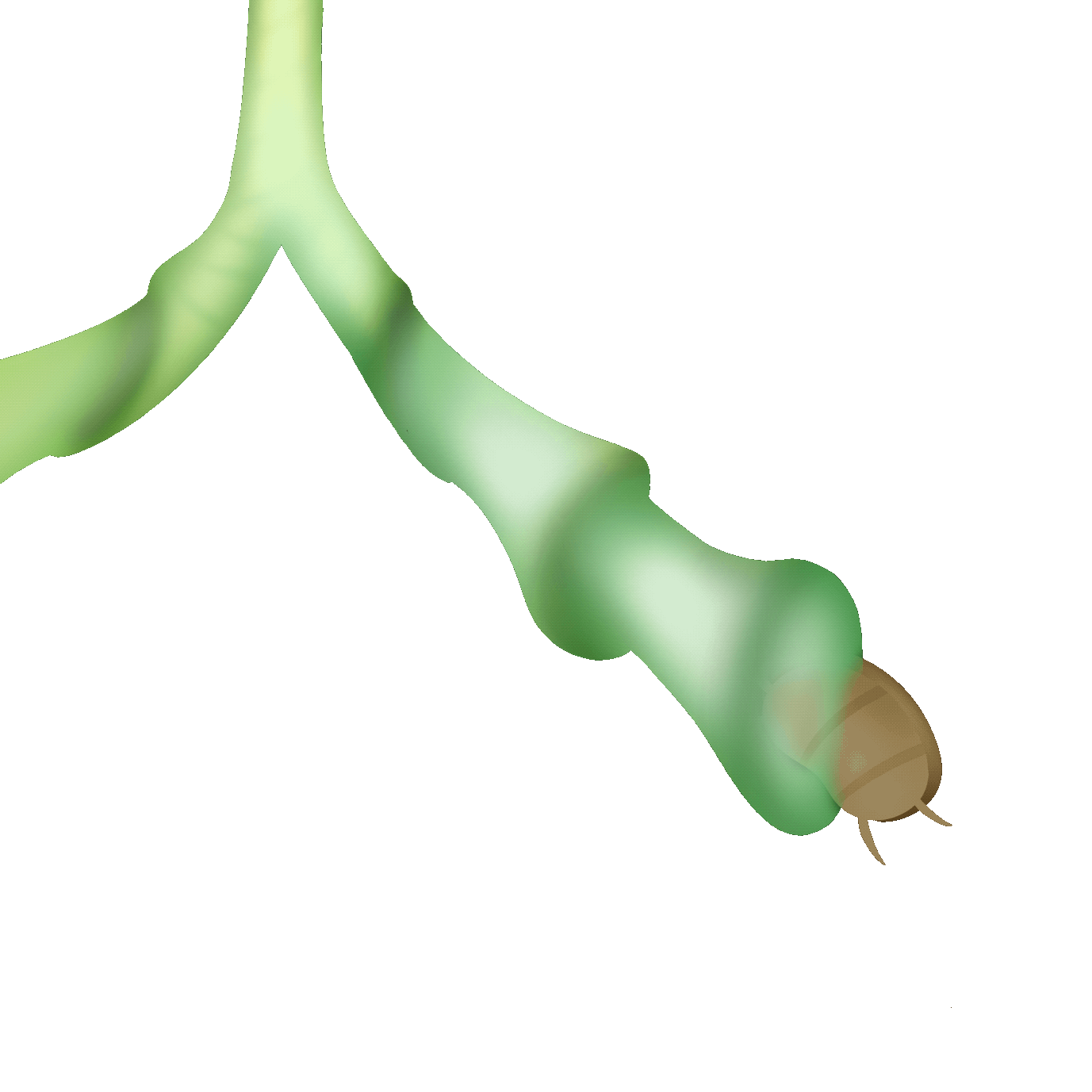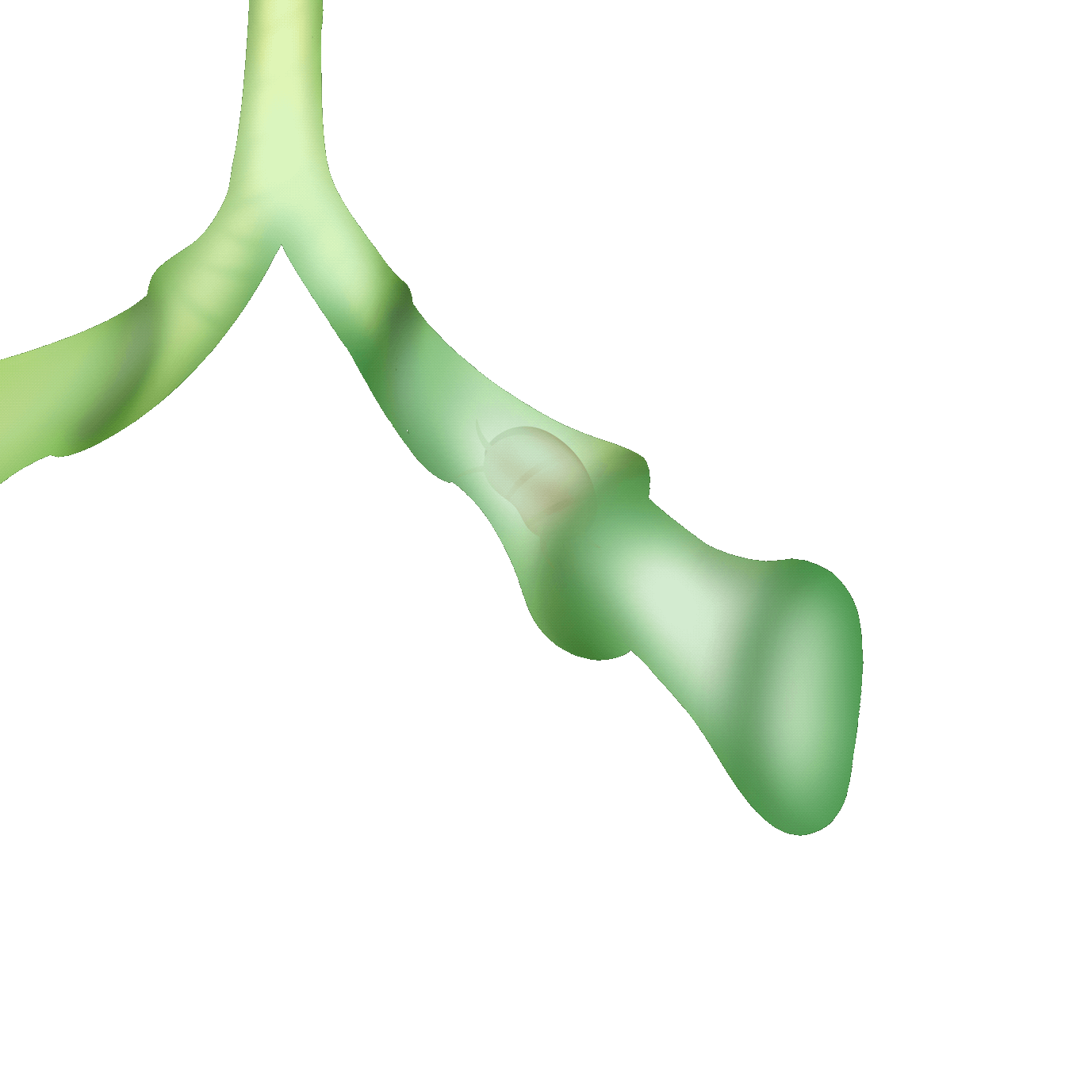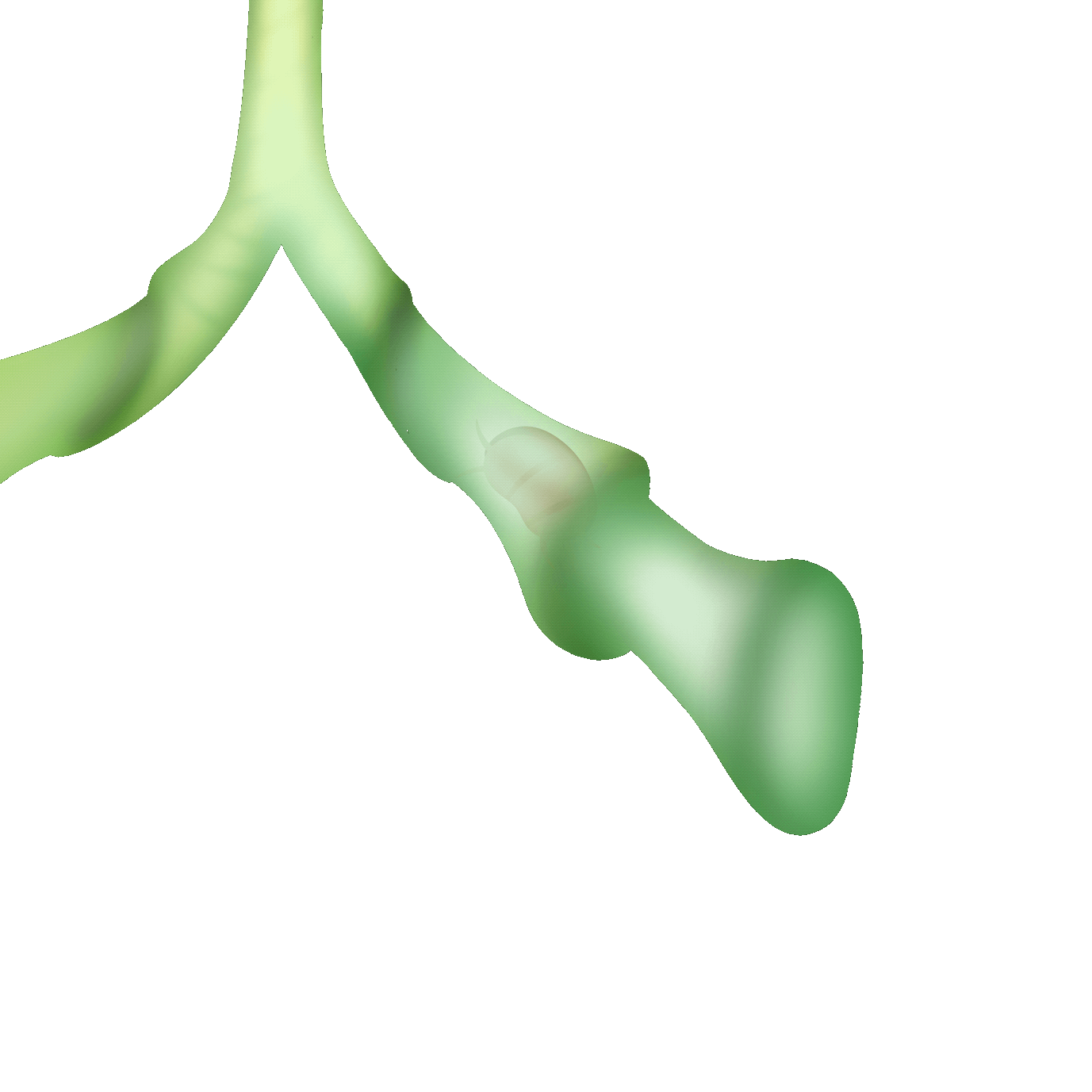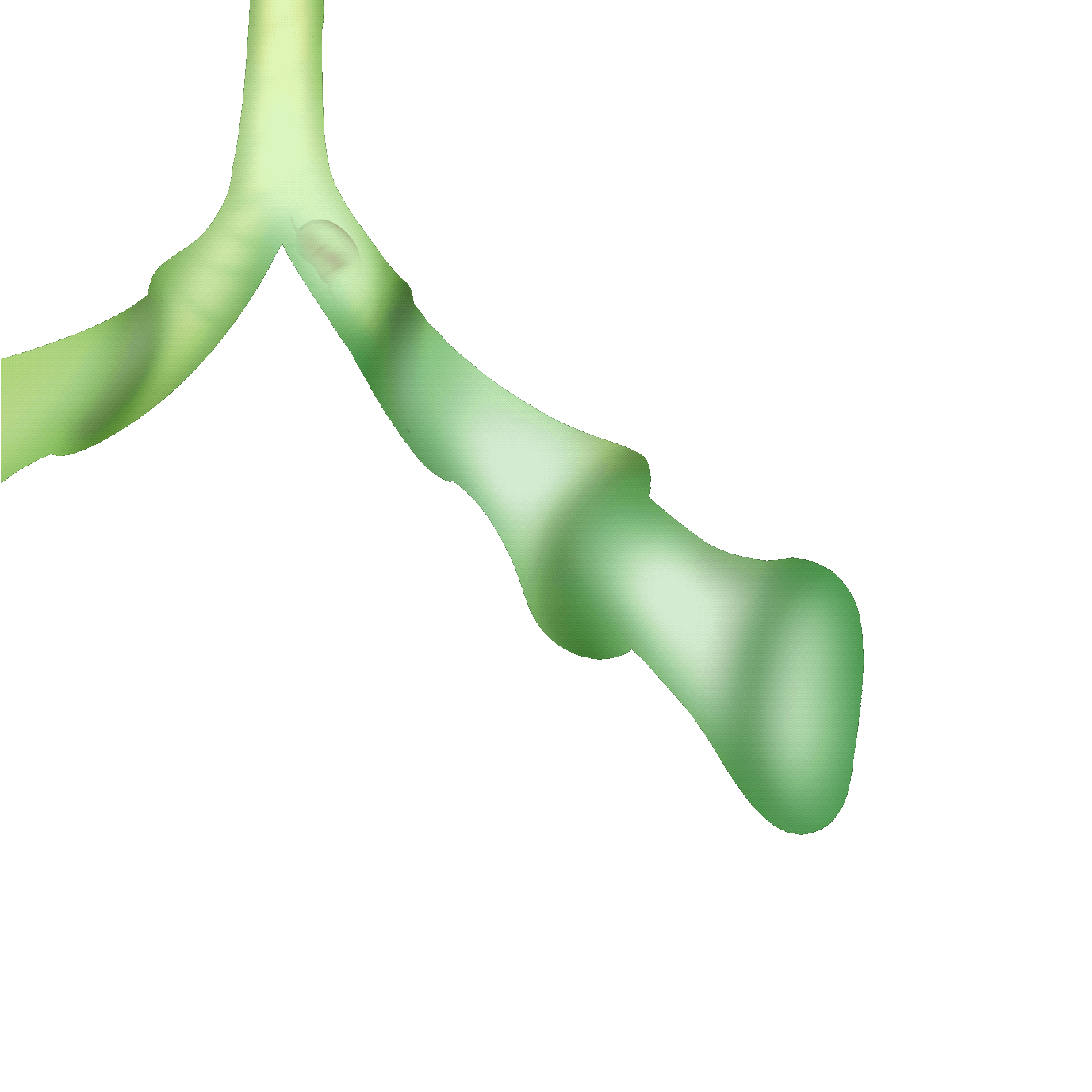
蝦籠式
Corkscrew traps
也有人稱之為「迷宮式」,透過「開口大、內側小」的機制捕捉獵物,誘導小蟲進入陷阱迷宮而無法退出。它們的瓶壁內側有著堅硬的導引毛,逼迫獵物只能順著毛進入到更深處,無路可退最後被消化吸收。
Also known as the "labyrinth trap," this mechanism uses a "large opening, narrow inside" design to capture prey, leading small insects into the trap's labyrinth, where they cannot escape. The inner walls of the trap are lined with rigid guiding hairs, forcing the prey to follow the hairs deeper into the trap, with no way out, eventually being digested and absorbed.
植物秘境
Secret Realm of Plants
一片經過長期淋洗,而形成泥濘浸水的酸性貧瘠土地上,土壤中的氮和其它植物生長必須的營養鹽,不斷地被沖刷流失,原本生長在這片土地上的植物慢慢地因為養分不足而死亡,只有能夠從別處取得氮和營養鹽的植物才能存活下去。食蟲植物的形成是經過長時間演化與天擇的結果。食蟲植物的祖先為了適應缺乏養份(尤其是氮肥和磷肥)的酸性池沼或濕地生態環境,而演化發展出來的特殊生存之道,誘殺小動物來補充各種必需但環境缺乏的礦物質和酵素。
A piece of land that has been leached for a long time forms acidic, nutrient-poor soil that becomes waterlogged and muddy. In this environment, nitrogen and other nutrients necessary for plant growth are continuously washed away. The plants that originally grew on this land gradually die due to nutrient deficiency, and only plants that can obtain nitrogen and nutrients from elsewhere are able to survive. The formation of carnivorous plants is the result of long-term evolution and natural selection. The ancestors of carnivorous plants developed this special survival strategy in order to adapt to the nutrient-poor (especially nitrogen and phosphorus) acidic wetlands or bogs, evolving to attract and capture small animals to supplement essential minerals and enzymes that are lacking in the environment.


桃園濕地 Taoyuan Wetlands
小毛氈苔、長葉茅膏菜
Drosera spathulata Lab.、Drosera finlaysoniana.
金門田埔濕地 Kinmen Tianpu Wetland
長葉茅膏菜、寬葉毛氈苔、黃花狸藻、絲葉狸藻
挖耳草、短梗挖耳草
Drosera finlaysoniana、Drosera burmanni
Utricularia aurea Lour.、Utricularia gibba
Utricularia bifida、Utricularia caerulea L.
苗栗獅頭山
Miaoli Shitou Mountain
圓葉狸藻
Utricularia striatula.
新竹蓮花寺濕地
Lianhua Temple Wetland in Zhubei City, Hsinchu County
長葉茅膏菜、小毛氈苔
寬葉毛氈苔、短梗挖耳草
Drosera finlaysoniana
Drosera spathulata Lab.
Drosera burmanni
Utricularia caerulea L.
汐止新山夢湖
Xizhi Xinshan Dream Lake
黃花狸藻
Utricularia aurea Lour.
視覺設計
Visual Desing

原生食蟲植物幾乎為鮮綠及外來食蟲植物多數是明艷亮麗的色彩,則視覺顏色大膽採用翠綠、亮橘作為底色,整體以寫實插畫風格,透過插畫呈現細節部分,比如:花朵、構造及紋理讓大眾了解植物捕蟲特色和植物的奧妙。
Native carnivorous plants are mostly vibrant green, while many non-native species exhibit striking, bright colors. Therefore, the visual design boldly incorporates emerald green and vivid orange as the base colors. The overall style adopts realistic illustrations, highlighting intricate details such as flowers, structures, and textures. Through these illustrations, the project aims to showcase the unique insect-catching features of these plants and reveal their fascinating biological intricacies.


食蟲掛軸
Carnivorous PlantHanging Scroll
本設計推廣於食蟲植物生態知識和捕捉蟲子動畫,透過NFC數位感應觀看植物捕捉昆蟲的動畫導覽,探討食蟲植物獨特生態之美。
This design promotes ecological knowledge of carnivorous plants and features animations of their insect-catching mechanisms. Through NFC digital sensing, users can access guided ecological information, exploring the unique beauty of carnivorous plant ecosystems.
產品設計
Product Desing

整體製作物分別為食蟲立體書、食蟲植物介紹卡、食蟲掛軸、黏蟲體驗套組。在個包裝我們以綠色和橘色將原生種以及外來種做區分。
The complete set includes a carnivorous plant pop-up book, informational cards, a hanging scroll, and an interactive sticky-trap experience kit. In the packaging design, green and orange are used to distinguish native species from non-native species.
創意產品設計
Creative Product Design
透過產品設計,推廣食蟲植物獨特生存法則,設計兩款植物捕蟲系列產品,透過仿生設計造型和植物特色捕蟲概念,讓大眾了解植物在大自然中獨特生存方式。
Through product design, we promote the unique survival strategies of carnivorous plants. We have designed two insect-catching products inspired by these plants. By incorporating biomimetic design elements and the plants' natural insect-trapping mechanisms, we aim to help the public understand their distinctive survival methods in nature.



食蟲立體書
POP-UP BOOK
本設計主軸為立體書,推廣食蟲植物獨特性及結構造型美學,用摺頁方式呈現,採用立體結構、彩圖像營造食蟲植物的氛圍感,藉由立體造型結構傳達對於食蟲植物捕捉概念。
The core of this design is a pop-up book that highlights the uniqueness of carnivorous plants and their structural aesthetics. It is presented through foldable pages with three-dimensional structures and vibrant illustrations to create an immersive atmosphere. The pop-up elements visually convey the concept of how carnivorous plants capture their prey.


食蟲植物介紹卡
Plant introduction card
本次設計製作物為設計食蟲小卡,透過圖文資訊方式引領大眾了解食蟲植物背後鮮為人知的植物秘辛,探討食蟲植物捕蟲的獨特性。
This design project features a set of carnivorous plant informational cards. Through a combination of visuals and text, these cards guide the public in discovering the lesser-known secrets of carnivorous plants and exploring the uniqueness of their insect-catching mechanisms.

黏蟲體驗套組
Sticky insect experience set
本設計推廣食蟲植物造型美學,設計立體結構、仿生造型的黏蟲體驗套組,透過紙張立體拼圖產品體驗,傳達食蟲植物獨特性質和與產品的互動性。
This design promotes the aesthetic beauty of carnivorous plants through a 3D structured, biomimetic sticky-trap experience kit. By engaging with a paper-based 3D puzzle, users can explore the unique characteristics of carnivorous plants and interact with the product in an immersive way.
結語
Conclusion
透過本專題,希望能揭開台灣食蟲植物的神秘面紗,讓更多人認識並關注這些隱藏在森林、濕地與山間的奇特植物,進而提升生態意識,共同參與保育行動。
Through this project, we hope to unveil the mystery of Taiwan’s carnivorous plants, allowing more people to discover and appreciate these fascinating species hidden in forests, wetlands, and mountains. By raising ecological awareness, we aim to inspire collective participation in conservation efforts.




